1/26/11
We started off the day by turning UP pg 11 and 12. Next we filled out a sheet about the science class we are going to take next year. Then we began notes.
Notes:
- All life is connected
- Evolution is cause of today's diversity.
- Charles Darwin came up with the idea. He wrote "The origins of Species" in 1859.
- 2 main points in book:1. "decent with modification"(this means every descendent is a little different. 2. the mechanism for evolution is "natural selection"
- Darwin loved nature and traveled world in HMS Beagle." He observed species on different islands
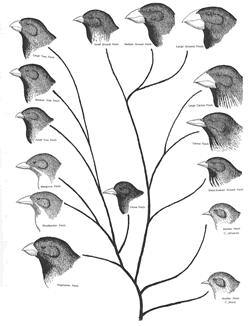
- saw variety of finches in the Galapagos Islands.
- After many generations, 2 populations could become dissimilar enough to be separate. (called divergent evolution)
- Darwin observed the finches' beaks and color.
- Natural selection- 3 main points:
- Overproduction- leads to struggle for existence among individuals of a population.
- Individuals in a population vary in traits, no 2 are alike.
- Individuals with best traits to survive leave greatest number of surviving offsprings.
- Nature decides what traits are most fit.
- Adaption is accumulation of favorable variation in a population over time.
- Darwin looked at Artificial Selection- Humans modify species to get best traits.
- In Artificial selection. humans change trait, not nature.
- natural selection today, i.e.= Pesticide- now some insects are immune to pesticide.
- Camouflage is an example of evolutionary adaption. (mantids)

- Evolution- 2 modern definitions:
- genetic composition changes over time
- all life descended from common ancestor
- Scientist during Darwin's time thought earth was young, and that Darwin's idea was radical
- Anizimander- Greek philosopher who though simpler forms of life preceded more complex life.
- Aristotle- Greek philosopher thought species were fixed and didnt evolve.
- Buffon- studied fossils. Said Earth is mush older. Said species in fossils were ancient versions of modern species.
- Lamarck- said the life evolves through adaptation.
- He said "Inheritance of Aquired Characteristics" (not using a body part would cause offspring to be born without that body part.
- Lyell-said ancient earth was sculpted by geologic process. (earthquake and mountains)
- Graualism principle.
- Wallace-developed concept of natural selection. Had same idea as Darwin but Darwin published his ideas before Wallace did.
- fossils- preserved remnants of impressions left by organisms that lived in the past.
- Younger strata are on top of the older ones. Level reveals "relative age"
- Fish like vertebrats are oldest, then amphibians, then reptiles, then mammals and birds.
- Paleontologist- scientise who studies fossils.
Homework: UP pg 5, E.C. pg 6 and/or M&M.
Next scribe: Katie