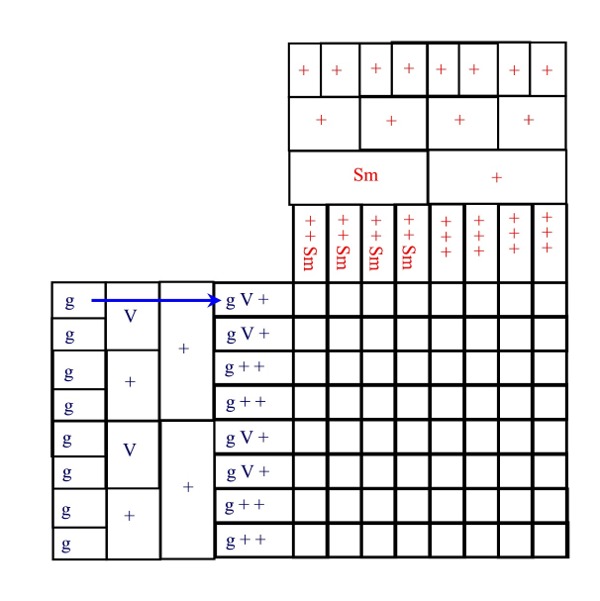
- A chart for reading genetic codes.... know how to read this for the test
- find first letter in center of circle
- find second letter in the 2nd row
- find third letter in 3rd row
- 61 codes for amino acids- 3 of them, UAA, UAG, and UGA tell the ribosomes to stop making the polypeptide
- AUG= Methionine but also provides signal to start a polypeptide chain
- Most codes are shared by all organisms
DNA Replication
- making exact copies of DNA in nucleus, occurs before cell division(mitosis/meiosis
enzyme= DNA polymerase
Transcription
- molecule of DNA is copied into a complementary strand of mRNA
enzyme=RNA polymerase

Steps of Transcription:
- Initiation- RNA polymerase attaches to the DNA promoter nucleotide sequence on DNA, RNA is made
- RNA elongation- RNA grows longer, peels away from DNA, DNA strands come back together
- Termination-RNA polymerase reaches the end of the gene (the terminator), polymerase molecule detaches from RNA molecule and the gene
- Prokaryotes- the mRNA is already ready
- Eukaryotes- need to proccess, add extra nucleotides
- cap and tail-protect RNA from enzymes, help ribosomes recognize it as mRNA
- introns- bad, noncoding regions
- exons- good, cooding regions
- RNA splicing- introns removed before RNA leaves nucleus
- Now mRNA is ready!!!!
Translation
- mRNA (Messenger RNA) translated into tRNA (Transfer RNA)
- mRNA goes to ribosome
- 2 subunits made of proteins and rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
- small subunit- binding site for mRNA
- large subunit- binding site for tRNA
- tRNA-twists and folds, end of folded molecule=anticodon
- anticodon recognizes codon on mRNA, then the other end of the tRNA is where an amino acid can attach
- Bonds between (AA)s ((amino acids)) are peptide bonds
- The polypeptide that is growing and forming is the protein!!
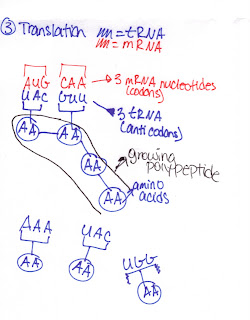
Steps of Translation:
- Initiation- mRNA binds to small ribosomal subunit, tRNA attached to amino acid binds to start codon, AUG on mRNA; large ribosomal subunit binds to small one, which creates a working ribosome
- Elongation- amino acids are added to the first amino acid, creating a polypeptide chain
- Termination- one of the stop codons tells the translation to stop. Polypeptide is freed ( many A.A), and ribosome splits into its subunits
RNA has:
- Ribose sugar
- 1 strand
- U instead of T
- smaller than DNA, can go inside/outside nucleus
- 3 types: mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
Homework:
- UP 99-110 due 12/2
- Pre-lab 37- cut out????
- DNA/ Chicago Tribune Project Due next Tues.